Understanding how AI Works
Part of: AI Learning Series Here
Quick Links: Resources for Learning AI | Keep up with AI | List of AI Tools
Subscribe to JorgeTechBits newsletter
Summary: Artificial Intelligence (AI) is all around us already, and it’s only going to become more prevalent in the years to come. By leveraging the power of machine learning and other AI algorithms, we can create tools and applications that are more intelligent, more accurate, and more effective than ever before. Whether you’re using a chatbot to schedule a doctor’s appointment or a virtual assistant to control your smart home devices, you’re interacting with AI technology in a very real way. ChatGPT is the latest in a series of implementations that capture our imagination.
Outside the many conversations about pro and cons of Artificial Intelligence technology, understanding how it works is important. It is not magic; it is technology that has been in development and research for many decades.
See my 101-level presentation on this topic: Impact of AI below:
Definition
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a broad term that encompasses various technologies and techniques aimed at enabling machines to perform tasks that typically require human-like intelligence. It is a field of computer science that seeks to develop algorithms and systems that can perform tasks that require intelligence, such as recognizing speech, making decisions, and understanding natural language. However, AI is not a single technology, but rather a collection of various technologies and techniques that work together to enable machines to perform intelligent tasks.
What makes AI technology different from other types of software?
The answer lies in their ability to learn and adapt over time. Unlike traditional software, which is programmed to follow a set of rules and instructions, AI technology is designed to learn from experience and improve over time.
This is why AI technology is so important, and controversial at times. By leveraging the power of machine learning and other AI algorithms, we can create tools and applications that can learn from vast amounts of data and become more accurate and effective over time. This has the potential to transform, and frankly speaking disrupt, every field, job and industry including creatives, content producers, healthcare, finance, and education.
Who is using AI technology today?
Just about everyone! If you’ve ever used Siri, Alexa, an annoying automated customer service (chatbot), chances are that you’ve interacted with artificial intelligence (AI) technology.
From healthcare providers to financial institutions to tech companies, there are a wide variety of industries that are leveraging the power of AI to improve their products and services. For example, some healthcare providers are using chatbots to help patients with non-emergency medical inquiries, such as scheduling appointments or getting information about prescription medications. Banks and financial institutions are using chatbots to provide customer service and support for banking transactions, such as checking account balances and transferring funds.
Chatbots are AI-powered programs that can converse with users using natural language. They’re used in a variety of industries, from customer service to healthcare to education. One example of a chatbot is Grammarly, which uses AI to help users write better and more grammatically correct sentences.
Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant. These tools incorporate chatbot technology, but they’re also designed to perform a wide range of tasks and functions beyond just answering questions and providing information. They call can set reminders, send messages, make phone calls, and even control smart home devices.
AI has come a long way in recent years and even more in recent months. Now there is a wide variety of AI-powered tools and applications that we use every day.
How does the AI work?
At its core, AI relies on advanced algorithms to perform two tasks:
- Understand and respond to user queries: language processing and
- Learn, catalog and process data: machine learning.
Natural language processing (NLP) allows the AI to understand and interpret natural language input from users.
Machine learning processes enables the AI to learn and improve over time using a broader range of algorithms that can be used for a variety of tasks including deep learning, which uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers to learn complex representations of data.
Natural language models (NLMs) is a type of machine learning model that is specifically designed to process and understand natural language. NLMs use statistical methods to analyze large amounts of text data and identify patterns in language usage, which allows them to learn and understand how language works.
A deep neural network (DNN) is often used as the architecture for an NLM. It is a type of neural network that consists of multiple layers of interconnected neurons. DNNs are commonly used for tasks such as image recognition, speech recognition, and natural language processing. The architecture of a DNN is designed to extract and transform features from complex data, which can be used for prediction, classification, or clustering.
NLM and a DNN are not the same thing, they are often used together in natural language processing to create powerful language models that can perform a wide range of tasks, such as language translation, text generation, and sentiment analysis.
Training sets for NLMs can consist of a wide variety of text data, ranging from books and articles to social media posts and chat logs. The size of the training set for a NLM can vary depending on the specific model and the task it is being trained for. Generally, larger training sets can lead to better performance, as they provide more examples for the model to learn from and can capture a wider range of linguistic patterns and structures.
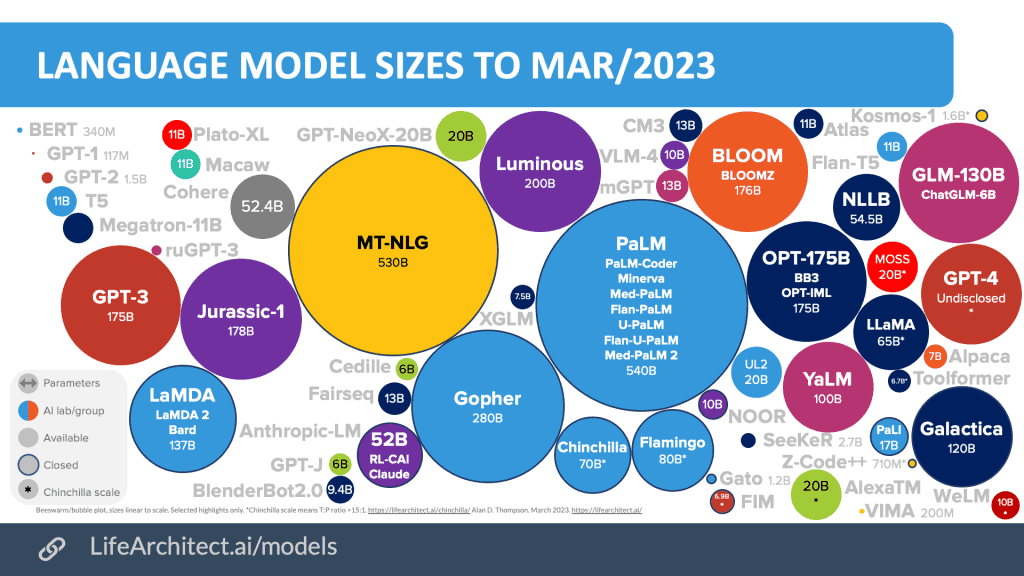
Source: Inside language models (from GPT-4 to PaLM) – Dr Alan D. Thompson – Life Architect
A foundation model is a type of pre-trained language model that serves as a starting point for building more specialized language models. Foundation models are typically trained on large, diverse datasets and are designed to capture general patterns and structures in language.
Currently, the most common type of language model is the transformer model, which was introduced in 2017 and is used in many of the most advanced natural language processing (NLP) systems today. Some of the most popular transformer models include BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) developed by Google, GPT-3 (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3) developed by OpenAI, and T5 (Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer) developed by Google.
What about ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is a topic of conversation that are on fire right now.
It is incredible that something that is less than 6 months old (as of this writing) this implementaitonof a chatbot that can carry on natural language conversations with users in a wide range of contexts and topics, has captured everyone’s attention on every field of humanity.
Please go to my ChatGPT article to continue reading…
Resources:
Presentation: Impact of AI
Inside language models (from GPT-4 to PaLM) – Dr Alan D. Thompson – Life Architect